Bilateral Retinal Astrocytic Hamartoma in Patient with Retinitis Pigmentosa: A Case Report
Poster Presentation - Case Report - Resident
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.35749/wacwsz10Keywords:
Case Report, Retinitis Pigmentosa, Retinal Astrocytic HamartomasAbstract
Abstract
Introduction : Retinal astrocytic hamartomas (RAH) are benign tumors derived from glial cells. It is usually asymptomatic and detected incidentally during screening patients with visual impairment. The variety of lesions in these tumors poses special challenges in their diagnosis and treatment. Modern imaging methods, including as spectral domain optical coherence tomography (OCT), have substantially increased knowledge of these lesions. The aim of this case report is to report a case of retinal astrocytic hamartoma with retinitis pigmentosa in a male patient.
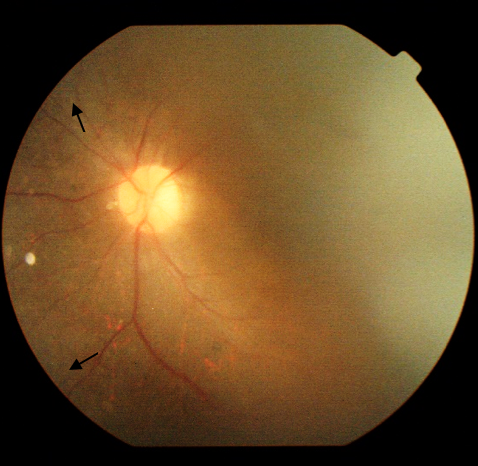
Case Illustration : A 22-year-old man presented with blurred vision with headache for 2 weeks accompanied by floaters, flashes of light and night blindness and the UCVA was 20/100 on both eyes. On fundoscopic examination, we found a well-defined multilobulated lesions with cystic impressions on optic nerve head, arteriolar attenuation, and bone spicule pigmentation in peripheral retina. Ultrasonography examination showed a hyperechoic mass with acoustic shadow on optic nerve head. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) showed hyper-reflective intraretinal mass with “moth-eaten pattern”. Electroretinogram's (ERG) patient showed reduction of a-wave and b-wave. Patient then referred to Low Vision and was given glasses.
Discussion : Retinal Astrocytic Hamartoma (RAH) is a benign tumor of the astrocytes and found within the nerve fiber layer of the retina. It is associated with certain types of phakomatosis but also in Retinitis Pigmentosa. Retinitis Pigmentosa can cause visual impairment as illustrated in this case.
Conclusion : Retinal astrocytic hamartomas of the optic nerve head have been described in patients with retinitis pigmentosa. The tumors can be found anywhere. A comprehensive evaluation and examination are required.
Downloads
References
(-)
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.