Anterior Orbitotomy with Transcutaneous Approach as Management of Orbital Cavernous Hemangioma
Poster Presentation - Case Report - Resident
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.35749/7ss9mn24Keywords:
Orbital cavernous hemangioma, Anterior orbitotomyAbstract
Introduction : Orbital cavernous hemangioma is the most common benign orbital lesion in adults. Management of cavernous hemangioma depends on the presented symptoms. Visual impairment is indication of surgical management. Anterior orbitotomy is the preferred surgical technique for cavernous hemangioma.
Case Illustration : A 34-years-old male came with chief complaint of mass in the inferior palpebra left eye (LE) accompanied with double vision for three years. Visual acuity of the right eye (RE) was 1.0 and LE was 0.8. Ophthalmology examination revealed hypertropia, non-axial proptosis, mass lesion sized 4 x
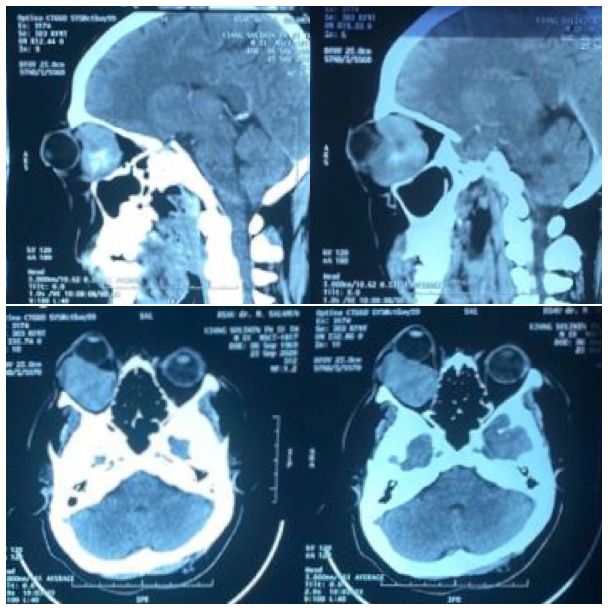
2 cm in the left inferior palpebra and RAPD grade I in the LE (Figure 1). Funduscopy examination in both eyes was within normal limit. CT-Scan examination showed intraconal and extraconal inhomogen mass lobulated in the left inferomedial which obliterate inferior and medial rectus muscle (Figure 2). Patient was diagnosed with proptosis and compressive optic neuropathy in LE caused by suspected orbital cavernous hemangioma. Anterior orbitotomy with transcutaneous approach was done (Figure 3). Histopathological examination showed proliferation of large blood vessels lined with endothelial cells as characteristic of cavernous hemangioma (Figure 4). There was improvement of visual acuity and no RAPD after surgery (Figure 5).
Discussion : Orbital cavernous hemangioma can compress optic nerve which will cause visual disturbances. Anterior orbitotomy with transcutaneous approach provides wider space when surgeon take out hemangioma completely. It will reduce bleeding caused by truncated mass of hemangioma and increase successful rate of surgery.
Conclusion : Anterior orbitotomy with transcutaneous approach can correct globe displacement and visual disturbances caused by orbital cavernous hemangioma.
Downloads
References
(-)
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.