Scleral Contact Lens for Steven-Johnson Syndrome
A Case Report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.35749/journal.v48i2.100460Keywords:
scleral contact lens, steven-johnson syndrome, dry eyesAbstract
Background: Steven-Johnson syndrome is one of life-threatening skin abnormality. SJS complication involve multiorgan disfunction such as mucosa, ocular, respiration, and digestive tract. Around 30- 50% of SJS patient experience chronic ocular sequel, which concludes progressive symblepharon, margo palpebral keratinization, trichiasis, entropion, corneal pannus, dry eye syndrome, and persistent epithelial cornea defect. Scleral contact lenses has beneficial in managing SJS patient, on both acute and chronic phases.
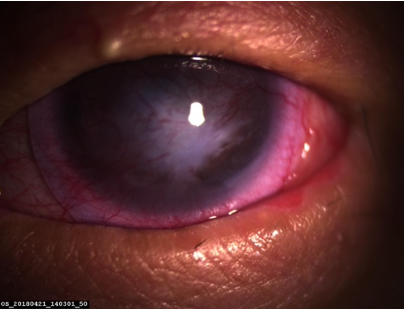
Methods: A 36-year-old female patient with SJS, presented for eye examination due to unpleasant sensation on both of their eyes and unsatisfactory quality of her vision. She presented high myopia, margo palpebral keratinization with trichiasis and distichiasis, symblepharon and hyperemic conjunctiva, wide corneal scar, and ocular neovascularization. A diagnostic trial set was used in the fitting process, and she was assessed according to standardized fitting methodology. Visual acuity, corneal topography, biometry, and ocular aberrations were evaluated. The follow-up period was 12 months.
Results: The best corrected visual acuity was 20/60 with correction lens S – 1.00 D for the left eye (LE) and 20/25 cannot be corrected with correction lens for the right eye (RE). After corneal contact lens fitting, visual acuity was improved to 20/20 and 20/25 for the RE and LE, respectively. The patient wore these contact lenses an average 8 hours a day. The patient’s dry eye complaint was significantly decrease with more comfortable ocular sensation
Conclusion: The present case report describes how the patient had scleral contact lens fitted successfully for management of SJS ocular complication. They provided optimal visual quality and restore the patient’s comfort.
Downloads
References
Creamer D et al: UK guidelines for the management of Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis in adults 2016. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2016; 69(6):e119-153
Ellender RP et al: Clinical considerations for epidermal necrolysis. Ochsner J 2014: 14(3):413-7
Arstikaitis MJ. Ocular aftermath of Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Arch Ophthalmol 1973;90:376-9 ?
Iyer G, Srinivasan B, Agarwal S, et al. Comprehensive approach to ocular consequences of Stevens Johnson Syndrome - the aftermath of a systemic condition. Graefes Arch Klin Exper Ophthalmol 2014;252:457-67
Papakostas TD, Le HG, Chodosh J, Jacobs DS. Prosthetic replacement of the ocular surface ecosystem as treatment for ocular surface disease in patients with a history of Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. Ophthalmology 2015;122:248-53?
Sotozono C, Yamauchi N, Maeda S, Kinoshita S. Tear exchangeable limbal rigid contact lens for ocular sequelae resulting from Stevens- Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis. Am J Ophthalmol 2014;158:983-993.e1?
Heur M, Bach D, Theophanous C, Chiu GB. Prosthetic replacement of the ocular surface ecosystem scleral lens therapy for patients with ocular symptoms of chronic Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Am J Oph- thalmol 2014;158:49-54
Tougeron-Brousseau B, Delcampe A, Gueudry J, et al. Vision-related function after scleral lens fitting in ocular complications of Stevens- Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Am J Ophthalmol 2009;148:852-859.e2 ?
Lopez-Garcia JS, Rivas Jara L, Garcia-Lozano CI, et al. Ocular features and histopathologic changes during follow-up of toxic epidermal nec- rolysis. Ophthalmology 2011;118:265-71 ?
Chang YS, Huang FC, Tseng SH, et al. Erythema multiforme, Stevens- Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis: acute ocular man- ifestations, causes, and management. Cornea 2007;26:123-9 ?
Romero-Rangel T, Stavrou P, Cotter J, Rosenthal P, Baltatzis S, Foster CS. Gas-permeable scleral contact lens therapy in ocular surface disease. Am J Ophthalmol 2000;130:25–32
Arstikaitis MJ. Ocular aftermath of Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Arch Ophthalmol 1973;90:376-9 ?
Fu Y, Gregory DG, Sippel KC, et al. The ophthalmologist’s role in the management of acute Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Ocul Surf 2010;8:193-203 ?
Di Pascuale MA, Espana EM, Liu DT, et al. Correlation of corneal complications with eyelid cicatricial pathologies in patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis syndrome. Ophthalmology 2005;112:904-12
Iyer G, Pillai VS, Srinivasan B, et al. Mucous membrane grafting for lid margin keratinization in Stevens-Johnson syndrome: results. Cornea 2010;29:146-51
Iyer G, Srinivasan B, Agarwal S, et al. Comprehensive approach to ocular consequences of Stevens Johnson Syndrome - the aftermath of a systemic condition. Graefes Arch Klin Exper Ophthalmol 2014;252:457-67
Fu Y, Liu J, Tseng SC. Oral mucosal graft to correct lid margin path- ologic features in cicatricial ocular surface diseases. Am J Ophthalmol 2011;152:600-608.e1
Segal O, Barkana Y, Hourovitz D, et al. Scleral contact lenses may help where other modalities fail. Cornea 2003;22:308–10
Rathi VM, Mandathara PS, Dumpati S, Vaddavalli PK, Sangwan VS. Boston ocular surface prosthesis: An Indian experience. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2011;59:279–81
Stason WB, Razavi M, Jacobs DS, Shepard DS, Suaya JA, Johns L, Rosenthal P. Clinical benefits of the Boston Ocular Surface Prosthesis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010;149:54–61
Papakostas TD, Le HG, Chodosh J, Jacobs DS. Prosthetic replacement of the ocular surface ecosystem as treatment for ocular surface disease in patients with a history of Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. Ophthalmology 2015;122:248–53
?Sotozono C, Yamauchi N, Maeda S, Kinoshita S. Tear exchangeable limbal rigid contact lens for ocular sequelae resulting from Stevens- Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis. Am J Ophthalmol 2014;158:983–93
?Heur M, Bach D, Theophanous C, Chiu GB. Prosthetic replacement of the ocular surface ecosystem scleral lens therapy for patients with ocular symptoms of chronic Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol 2014;158:49–54
Campbell R, Caroline P. RGP scleral lenses for Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Contact Lens Spectrum. 1997 May
Fine P, Savrinski B, Millodot M. Contact lens management of a case of Stevens-Johnson syndrome: a case report. Optometry. 2003 Oct;74(10):659–64
Lim P, Ridges R, Jacobs DS, Rosenthal P. Treatment of persistent corneal epithelial defect with overnight wear of a prosthetic device for the ocular surface. Am J Ophthalmol 2013;156:1095–101
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Tri Rahayu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
