Evaluation of Cup Disc Ratio and RNFL Thickness Based on Goldmann Visual Field Test
Abstract
Introduction and Objective : To assess the relationship between the cup-disc ratio of the optic nerve head and peripapilarry RNFL thickness to the visual field loss in glaucoma patients.
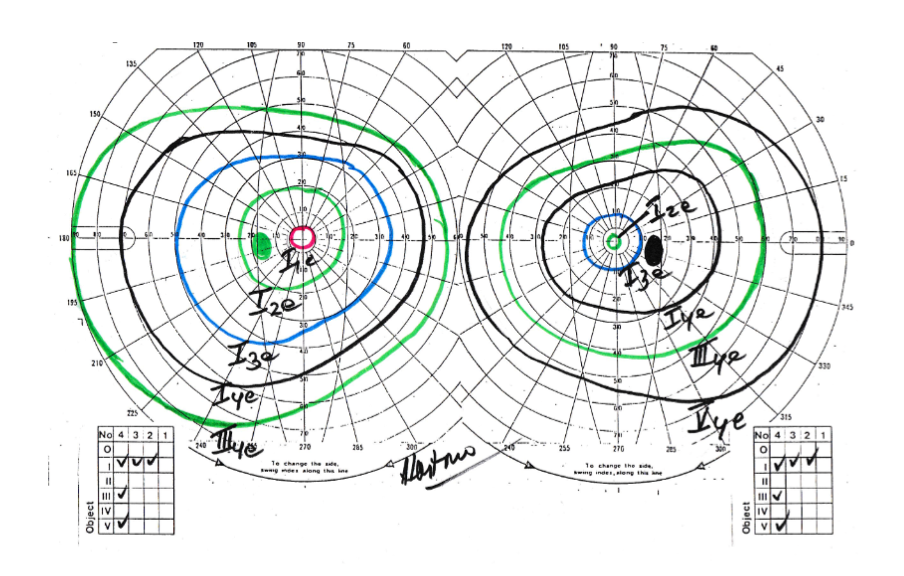
Methods : Visual field from Goldmann kinetic perimerty and Ocular Computed Tomography (OCT) records from Yap Eye Hospital, Yogyakarta are used to examine the figure of visual field loss in glaucoma patient.
Result: Broad spectrum of glaucoma-related visual field defects were observed from 73 eyes. The most common visual field defects are arcuate defect (23.3%) and followed by general depression. Arcuate defects can already observable in some patients with cup-disk ratio of 0.5 (30%).Arcuate defect occurs in the average RNFL thickness of 69.90 ?m (46.93-118.77). It appears that the pinhole vision appeared on the average RNFL thickness of 44.23 ?m (25.33-63.13), and temporal RNFL thickness remnant occured at 48.64 ?m (46.22-51.06). RNFL thickness with normal visual field was on the thickness of 107.78 ?m (100.27-115.29).
Conclusion: Visual field defect that may be observed in glaucoma with Goldmann kinetic perimetry are arcuate defect, and general visual field depression. RNFL thickness may be correlated longitudinally with the worsening of visual field defect.
Full text article
References
Basic and clinical science course Section 10 Glaucoma. San Francisco: American Academy of Ophthalmology. 2019. 18 p.
Xu G, Weinreb RN, Leung CK. Optic nerve head deformation in glaucoma: the temporal relationship between optic nerve head surface depression and retinal nerve fiber layer thinning. Ophthalmology. 2014 Dec 1;121(12):2362-2370.
Medeiros FA, Zangwill LM, Bowd C, Vessani RM, Susanna Jr R, Weinreb RN. Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer, optic nerve head, and macular thickness measurements for glaucoma detection using optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005;139(1):44-55.
Zangwiil LM, Bowd C, Weinreb RN. Evaluating the optic disc and retinal nerve fiber layer in glaucoma II: optical image analysis. Taylor & Francis. 2000. (Vol. 15, No. 4, pp. 206-220).
Caprioli J, Miller JM, Sears M. Quantitative evaluation of the optic nerve head in patients with unilateral visual field loss from primary open-angle glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 1987;94(11):1484-1487.
Sommer A, Katz J, Quigley HA, et al. Clinically detectable nerve fiber atrophy precedes the onset of glaucomatous field loss. Arch Ophthalmol 1991;109(1):77–83.
Turalba AV, Grosskreutz C. A review of current technology used in evaluating visual function in glaucoma. Semin Ophthalmol 2010; 25(5–6):309–316.
Quigley HA, Addicks EM, Green WR, Maumenee AE. Optic nerve damage in human glaucoma: II. The site of injury and susceptibility to damage. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981; 1;99(4):635-649.
Bowd C, Weinreb RN, Williams JM, Zangwill LM. The retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in ocular
;118(1):22-26.
BudenzDL,AndersonDR,VarmaR,SchumanJ,CantorL,SavellJ,GreenfieldDS,PatellaVM,Quigley HA, Tielsch J. Determinants of normal retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by Stratus OCT. Ophthalmology. 2007: 30;114(6):1046-1052.
Quigley HA, Katz J, Derick RJ, Gilbert D, Sommer A. An evaluation of optic disc and nerve fiber layer examinations in monitoring progression of early glaucoma damage. Ophthalmology. 1992;99(1):19-28.
Nils A. Loewen MD, P. A. Clinical Glaucoma Care- The Essentials. New York: Springer. 2014. 118 p.
TuulonenA, AiraksinenPJ. Initial glaucoma to us optic disk and retinal nerve fiber layer abnormalities and their progression. Am j ophthalmol. 1991;111(4):485-490.
Ramirez M, Chaya C, Gordon L & Giaconi J (2008): A comparison of semiautomated versus manual Goldmann kinetic perimetry in patients with visually significant glaucoma. J Glaucoma 17: 111–117.
Nowomiejska K, Brzozowska A, Zarnowski T, Rejdak R, Weleber RG & Schiefer U (2012): Variability in isopter position and fatigue during semi-automated kinetic perimetry. Ophtalmologica 227: 166–172.
Authors
Copyright (c) 2022 Tatang Talka Gani, Retno Ekantini, Hartono Hartono, Krisna Dwi Purnomo Jati

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.