COMPARISON OF ONH, MACULA STRUCTURE AND HFA PATTERN IN HIGH MYOPIA AND EMETROPIA EYES WITH/WITHOUT GLAUCOMA
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.35749/journal.v49i1.100557Keywords:
myopia, OCT, GlaucomaAbstract
Introduction: Axial length elongation contributes a challenge in myopia eyes due to morphological and visual field abnormalities. OCT instruments do not embed a normative database from high myopia. The study is aimed to compare Cirrus OCT and HFA parameters on high myopia and emetropia with/without glaucoma.
Methods: This cross-sectional, prospective study was conducted at Sardjito General Hospital from 1st April 2021 to 11th May 2021. Patients with high myopia was enrolled with Spherical Equivalent (SE) ? -6D, 20 – 55 years of age. All participants underwent a complete ophthalmologic examination. Inclusion criteria: BCVA 20/40 or better, reliable visual field results.
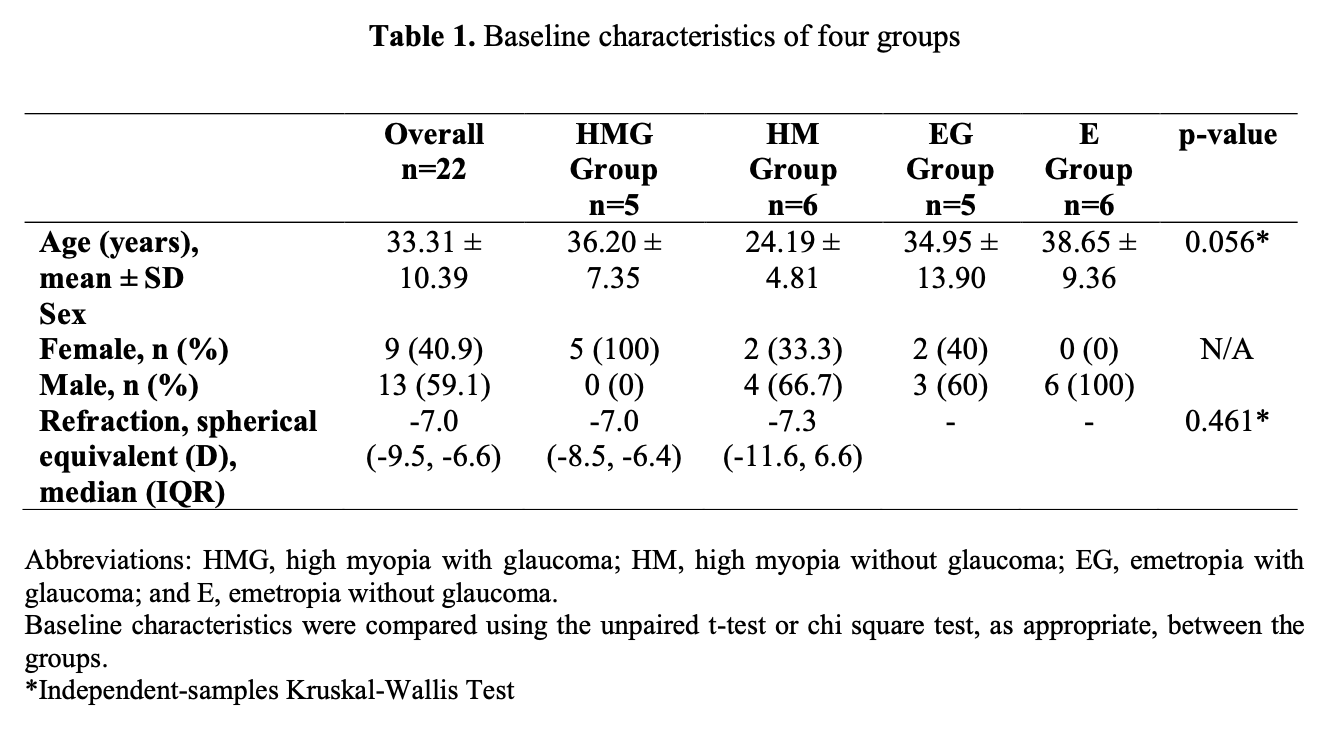
Result: From 22 eyes, there were no significant difference of age between high myopia with glaucoma/HMG (n=5), high myopia/HM (n=6), emetropia with glaucoma/EG (n=5), emetropia/E (n=6) with mean age was 36±3.2 y.o and 60% were male with SE -8.5±1.03D. Among ONH parameters, there were no differences between groups. In HMG, HM, EG, E group, median avgRNFL was 85um, 96.5um, 105um, 110um respectively. Thus, median vertical CD is 0.48, 0.40, 0.58, 0.55 in HMG, HM, EG, E group respectively. Whilst median GCIPL and visual index were 75um, 78.5um, 85um, 89.5um in HMG, HM, EG, E group respectively and had significantly different 0.012 (p<0.05) between groups. Median visual field index was 92%, 97%, 98% in HMG, HM, EG group respectively with significantly different 0.04 (p<0.05).
Conclusion: The GCIPL and visual field index are significantly different between high myopia and emetropia with/without glaucoma
Downloads
References
Ng DSC, Cheung CYL, Luk FO, et al. Advances of optical coherence tomography in myopia and pathologic myopia. Eye. 2016: 30; 901-916.
Shoji T, Sato H, Ishida M, et al. Assessment of glaucomatous changes in subject with high myopia using spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011; 52: 2
Leung CK, Cheng AC, Chong KK, et al. Optic disc measurements in myopia with optical coherence tomography and confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48:3178–3183.
Hoh ST, Lim MC, Seah SK, et al. Peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness variations with myopia. Ophthalmology. 2006;113:773–777.
Kang SH, Hong SW, Im S, Lee S, Ahn MD. Effect of myopia on the thickness of the retinal nerve fiber layer measured by Cirrus HD optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010;51:4075–4083.
Strouthidis N, Vinciotti V, Tucker A, et al. Structure and function in glaucoma: The relationship between a functional visual field map and an anatomic retinal map. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016;47:12.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 idhayu anggit widhasari, krisna dwi purnomo, Tatang Talka Gani, Retno Ekantini

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
