Chemotherapy Compared with Radiotherapy as the First-line Therapy of Extranodal Marginal Zone Lymphoma: A Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.35749/journal.v48i2.100269Keywords:
Extranodal Marginal Zone Lympoma, Chemotherapy, RadiotherapyAbstract
Objective: To compare the efficacy and safety between chemotherapy and radiotherapy as the main therapy of Extranodal Marginal Zone Lymphoma (EMZL).
Method: Literature searching was conducted using PubMed, ScienceDirect, Google Scholar, ProQuest, and SpringerLink. All studies that met the inclusion and exclusion criteria were categorized based on the level of evidence. The data of demographic of the patients, staging of disease, type of treatments, and outcomes of this review including the number of local control rate, disease-free survival rate, overall survival rate, dosage, adverse drug reaction, complication and recurrence and/or relapses were also reported.
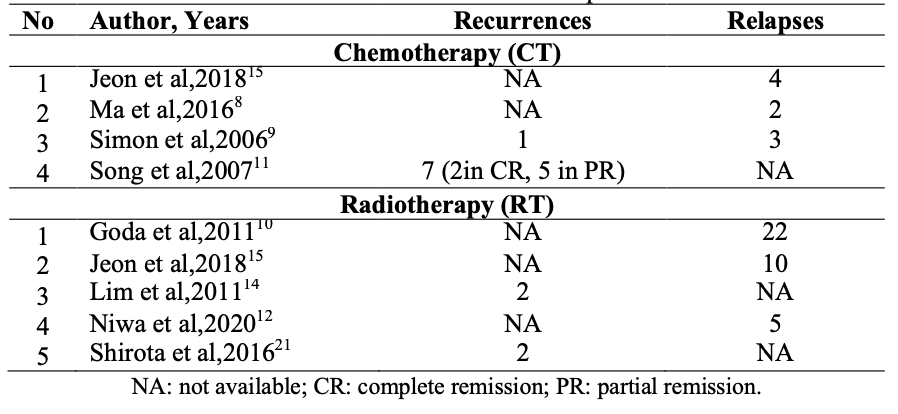
Result: From ten article, both radiotherapy and chemotherapy as the first-line treatment have high complete remission rate. Local control (complete remission) of chemotherapy group ranged from 56,25%-93,9%, while in radiotherapy group ranged from 70%-100%. Overal survival rate ranged from 92%-100% for chemotherapy group and 90,4%-100% for radiotherapy group. The most complication of the radiotherapy group were cataract formation, while the chemotherapy group showed systemic complications (hematologic or non-hematologic). The most relapse cases were shown in radiotherapy group.
Conclusion: Radiotherapy and chemotherapy showed high local control rates and survival outcomes especially in the early stages of extranodal marginal zone lymphoma (EMZL). Radiotherapy had a relatively higher incidence of ophthalmic complications that could interfere with patient’s quality of life. Therefore chemotherapy could be considered especially in younger patients.
Downloads
References
Decaudin D, De Cremoux P, Vincent-Salomon A, Dendale R, Lumbroso-Le Rouic L. Ocular adnexal lymphoma: A review of clinicopathologic features and treatment options. Blood. 2006;108(5):1451–60.
Rasmussen PK, Coupland SE, Finger PT, Graue GF, Grossniklaus HE, Honavar SG, et al. Ocular adnexal follicular lymphoma: A multicenter international study. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014;132(7):851–8.
Rosado MF, Byrne GE, Ding F, Fields KA, Ruiz PA, Dubovy SR, et al. Ocular Adnexal Lymphoma: A Clinicopathological Study of a Large Cohort of Patients with No Evidence for an Association with Chlamydia psittaci. Blood. 2005;107(2):167–72.
Annibali O, Sabatino F, Mantelli F, Olimpieri OM, Bonini S, Avvisati G. Review article: Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)-type lymphoma of ocular adnexa. Biology and treatment. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2016;100:37–45.
McKelvie PA. Ocular adnexal lymphomas: A review. Adv Anat Pathol. 2010;12(2):133–48.
Stefanovic A, Lossos IS. Extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of the ocular adnexa. Blood. 2009;114(3):501–10
Paik JS, Cho WK, Lee SE, Choi BO, Jung SE, Park GS, et al. Ophthalmologic outcomes after chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy in non-conjunctival ocular adnexal MALT lymphoma. Ann Hematol. 2012;91(9):1393–401.
Ma WL, Yao M, Liao SL, Tang JL, Wang YC, Kuo SH, et al. Chemotherapy alone is an alternative treatment in treating localized primary ocular adnexal lymphomas. Oncotarget. 2017;8(46):81329–42.
Ben Simon GJ, Cheung N, McKelvie P, Fox R, McNab AA. Oral Chlorambucil for Extranodal, Marginal Zone, B-Cell Lymphoma of Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue of the Orbit. Ophthalmology. 2006;113(7):1209–13.
Goda JS, Le LW, Lapperriere NJ, Millar BA, Payne D, Gospodarowicz MK, et al. Localized orbital mucosa-associated lymphoma tissue lymphoma managed with primary radiation therapy: Efficacy and toxicity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81(4):659–66.
Song EK, Kim SY, Kim TM, Lee KW, Yun T, Na II, et al. Efficacy of chemotherapy as a first-line treatment in ocular adnexal extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 2008;19(2):242–6.
Niwa M, Ishikura S, Tatekawa K, Takama N, Miyakawa A, Kubota T, et al. Radiotherapy alone for stage IE ocular adnexal mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas: Long-term results. Radiat Oncol. 2020;15:25–32.
Kim S-Y, Yang S-W, Lee W-S, Yang JW, Oh SY, Ahn HB, et al. Frontline treatment with chemoimmunotherapy for limited-stage ocular adnexal MALT lymphoma with adverse factors: a phase II study. Oncotarget. 2017;8(40):68583–90. 19
Lim SH, Kang M, Son J. Extranodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue type of the ocular adnexa: Retrospective single institution review of 95 patients. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2011;59:273–7.
Jeon YW, Yang HJ, Choi BO, Jung SE, Park KS, O JH, et al. Comparison of Selection and Long-term Clinical Outcomes Between Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy as Primary Therapeutic Modality for Ocular Adnexal MALT Lymphoma. EClinicalMedicine. 2018;4:32– 42.
Yahalom J, Illidge T, Specht L, Hoppe RT, Li YX, Tsang R, et al. Modern radiation therapy for extranodal lymphomas: Field and dose guidelines from the international lymphoma radiation oncology group. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015;92(1):11–31.
Cho WK, Lee SE, Paik JS, Cho SG, Yang SW. Risk potentiality of frontline radiotherapy associated cataract in primary ocular adnexal mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2013;92(1):11–31.
Hatef E, Roberts D, McLaughlin P, Pro B, Esmaeli B. Prevalence and nature of systemic involvement and stage at initial examination in patients with orbital and ocular adnexal lymphoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2007;125(12):1663–7.
Desai A, Joag MG, Lekakis L, Chapman JR, Vega F, Tibshirani R, et al. Long-term course of patients with primary ocular adnexal MALT lymphoma: A large single-institution cohort study. Blood. 2017;129(3):324–32.
Rigacci L, Nassi L, Puccioni M, Mappa S, Polito E, Dal Pozzo S, et al. Rituximab and chlorambucil as first-line treatment for low-grade ocular adnexal lymphomas. Ann Hematol. 2007;86:565–8
Shirota N, Nakayama H, Shiraishi S, Usui Y, Kimura K, Sanada T, et al. Target volume dose and clinical outcome in radiotherapy for primary marginal zone lymphoma of the ocular adnexa. Mol Clin Oncol. 2017;6(6):833–8.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Mutmainah Mahyuddin, Karina Luthfia, Neni Anggraini

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
